What is Rabies?
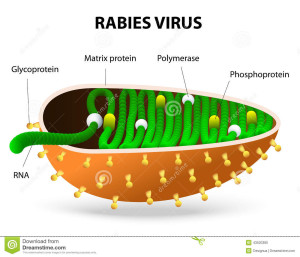
Rabies or Hydrophobia (fear of water) is a deadly disease caused by a virus called the Lyssa Virus. It is a bullet shaped virus as you can see in the diagram. It is primarily a disease occurring in the warm blooded animals like dogs, cats, jackals, wolves. The disease spreads to humans through bites or licks of Rabid animals. In humans the virus attacks the peripheral and central nervous system which includes all the nerves in our body leading to the classical fear of water (hydrophobia) and other symptoms as elaborated below. There is no cure for the disease once a person gets affected with Rabies and thus the person will eventually die. In this regard, Rabies becomes the only communicable disease in man which is 100% fatal.
Dogs are the main source of human infection accounting to 99% of the total. Though Rabies can also occur from the bites of wild animals like jackals, wolves, bats, the incidence of death is maximum after dog bites. Domestic animals like cats can also prove as a source of human infection if they get bitten by rabid stray dogs or rabid wild animals. In Asian and African countries, Dogs are the main villains behind Rabies. Whereas in the USA and Canada, Bats are the main culprits.
Transmission of Rabies
Haven’t you watched movies like “Who am I” and “World War Z” ? The transmission of Rabies happens in a very similar way if you know what I mean! The Rabies virus is excreted through the saliva of the affected animals. They accumulate in the salivary glands of these animals and are excreted in their saliva. When these animals bite humans, the virus in the saliva spreads and reaches the human body. Mere licks on skin surface, lips, other mucous membranes of human body are more than enough for the transmission to happen.
Dog handlers, veterinarians, hunters, laboratory workers handling infected specimens are at higher risk of getting infected with Rabies virus.
Human to human transmission can happen theoretically, but has not been confirmed yet. Ingestion of affected animal’s meat or ingestion of a Rabid cow’s milk are not potential sources of infection (provided they are not raw, but cooked).
Rabies Progression
Rabid animals always die within a few days of getting infected with the virus. The virus remains in the saliva of the animals for about 3 to 4 days. The journey of the virus is interesting. The virus spreads from the bite site to the peripheral nerves and through the peripheral nerves into the central nervous system which includes the spinal cord and the brain. Once the virus conquers the Nervous system, it then spreads to other parts of the body including the muscles, salivary glands etc. Invasion of salivary gland is necessary for transmission to take place (just like the zombies!). The time taken from the point of entry of the virus to the development of first symptoms of the disease (termed as the Incubation Period) is highly variable and depends on many factors. In fact, Rabies is the only disease where the Incubation Period is dependant on such high number of factors. Some of these factors are :
1- The site of bite – More dangerous and rapid onset of symptoms when the bite is at the face, head, neck, or the upper extremities.
2- The severity of bite – More dangerous if the bite is deep, and there are multiple bites.
3- Species of bites – More rapid progression in case of wild animals, but deaths are rare.
4- Cloth protection – can reduce the severity of the bite and thus the speed of progression of the disease.
5- Prevention – Anti Rabies Vaccine taken in the past can prevent one from getting the disease. Prompt interventions like giving Anti Rabies Serum immediately after the animal bite can also affect the Incubation Period.
Symptoms
The disease usually starts with minor headache, malaise, sore throat, and fever. Tingling sensation or pain at the bite site is one of the major complaints of affected persons. The next stage of the disease corresponds to the viral invasion of the central and peripheral nervous system. As a result of this, the patient develops many sensory, muscular and mental disturbances. Patient becomes intolerant to bright light, loud noise. Aerophobia (fear of air) can also occur. Fanning a current of air across the patient’s face results in violent contractions of the neck muscles. Increased sweating, salivation and tear formation are also seen in this stage.
Mental disturbances include anger, depression, irritability and fear of death.
Hydrophobia : Symptoms eventually becomes aggressive and finally the patient reaches a stage wherein all attempts of swallowing any kind of liquid becomes impossible. As the disease worsens, the mere sight or sound of water may provoke contractions of the muscles responsible for swallowing. This stage is referred to as Hydrophobia or Fear of Water and is one of the classical feature of Rabies.
The patient usually dies in 2 to 3 days.
As of date, there are only 3 persons alive who have survived Rabies.
Now, you must be familiar with Rabies, the transmission of the virus, the disease progression and the horrifying symptoms. If you are wondering how to prevent Rabies from happening after getting an animal bite, read this article which will elaborate on the immediate and essential steps to prevent Rabies.
Image Credit – CDC Global